Starting from the 1800s, our world has seen four major industrial revolutions – the age of mechanization, the age of science and mass production, the digital era, and what we are experiencing today, the age of automation. New technologies and advancements that have never been seen before are now taking the center stage around the world. Every industrial revolution aims to create a larger value-driven market while improving customer satisfaction, and the upcoming advancements in digital communication, Human Robot Collaboration and machine flexibility have played a pivotal role. While many nations around the world have begun implementing these new technologies, this article looks at how India has fared so far and where Industry 4.0 will take us.
What is Industry 4.0?
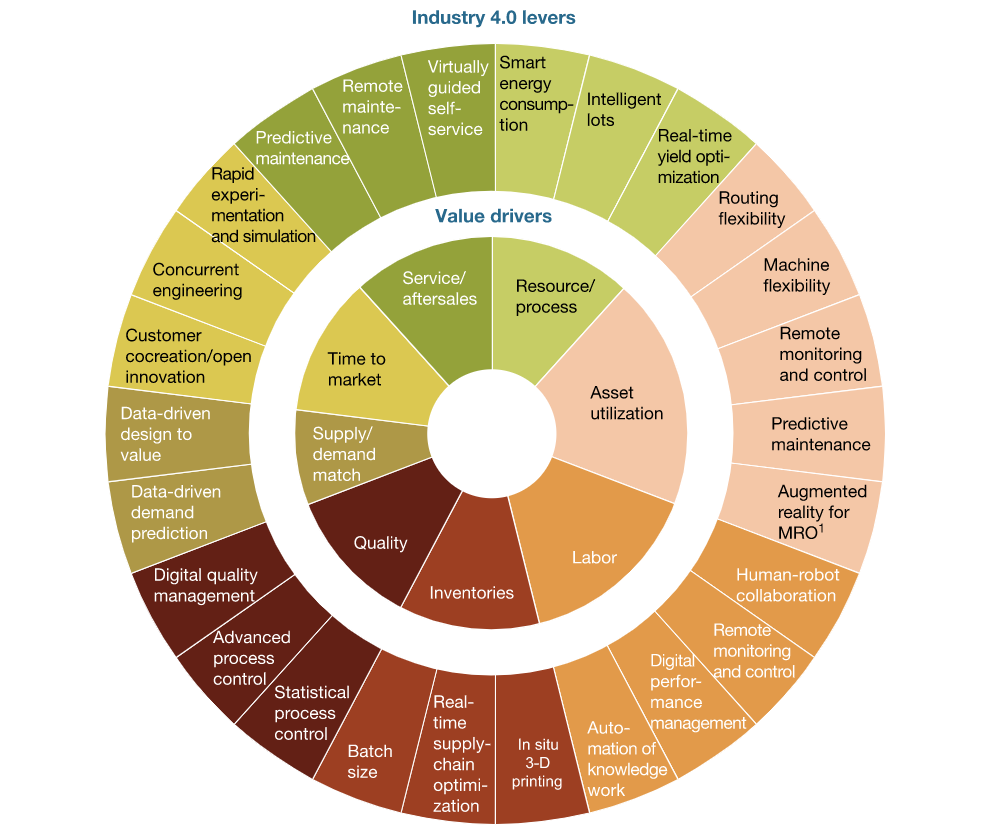
Industry 4.0 has multiple applications and to sort out which data is the most beneficial, manufacturing leaders utilize a “digital compass”. This consists of 8 basic value drivers and 26 practical Industry 4.0 levers as their solutions, as identified by McKinsey & Company. A brief description of these Industry 4.0 levers and solutions is as follows:
 Source: McKinsey & Company
Source: McKinsey & Company
-
Supply/Demand Match – It is highly important for companies to figure out the exact demand for their products, and how their competitors are faring. Technologies such as The Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine Learning have made it possible to capture a greater number of data points in order to improve the data driven demand prediction and data driven design to value.
-
Time to Market (TTM) – It is crucial to monitor the amount of time it takes for a product to reach its market after its conceptualization. This digital age has made it possible for companies to optimize and minimize their TTM by rapid experimentation and simulation, concurrent engineering, consumer co-creation and open innovation.
-
Service/Aftersales – An important growing aspect of the market is the value that is added by services and aftersales. Predictive maintenance, remote maintenance and virtually guided self-service are major solutions that contribute to over 90% of a company’s growth.
-
Resources and Process – Industry 4.0 provides a solution to the age-old question of ho w to produce in an efficient and less wasteful way. Manufacturers invest in smart energy consumption, smart pallets and real time yield optimization in order to minimize their costs and utilize resources.
-
Asset Utilization – One of the main applications of Industry 4.0 is asset utilization to improve the overall equipment efficiency. Routing flexibility, machine flexibility, remote monitoring and control, predictive maintenance and augmented reality for maintenance, repair and operation are the major solutions to this that have emerged in this new age of automation.
-
Inventory – Industry 4.0 has given a rise to data driven solutions and IoT, Big Data and 3D printing have taken the center stage in optimizing operations. Real-Time supply chain optimization, in situ 3D printing and real-time yield operations are being used today to analyze large amounts of data.
-
Quality – Quality control is one of the most important Industry 4.0 applications. With rising demands, manufacturers are shifting to statistical process control, advanced process control and digital quality management in order to mass produce with high quality.
-
Labor – Perhaps the most innovative applications of Industry 4.0 is automation and Human Robot Collaboration (HRC). Today, robots act as labor and perform tasks that are otherwise deemed unsafe for human employees. There is an immense potential for developments in this form of labor, and new technologies have paved the way for the emergence of collaborative robots, or cobots.
India and Industry 4.0
India has one of the largest labor forces in the world - around 40% of its population. With the introduction of Human Robot Collaboration, automation of knowledge work and digital performance management, Industry 4.0 has introduced new technologies that have vastly improved the quality of jobs by upskilling labor. As one of the largest economies in the world, manufacturers now need to focus on keeping up with the new advancements that are catapulting other economies to the top. The Indian Government aspires to drive the manufacturing sector to contribute to a quarter of the country’s entire GDP by 2025, skyrocketing it from the 16% sliver the industry takes up today. This is a journey that is estimated to create a whopping 100 million valuable jobs. To drive this mission, the Government has come up with many ambitious schemes, the most recent being “Atmanirbhar Bharat,” or “Self-Reliant India.” To harness the diverse potential of India’s vast population, initiatives like Digital India, Start-up India, and Skill India were also kickstarted. In order to do this however, India must start investing in Industry 4.0 solutions that provide quick and safe alternatives to the current manual processes and truly tap into the potential of its people.
One of the key tenets of the Industry 4.0 wheel developed by McKinsey & Company that India could truly benefit from is Human Robot Collaboration, or HRC. HRC is built on the concept that a human and a robot can work together in the same workspace, thus performing tasks in a collaborative manner. However, this is not possible with traditional industrial robots, which are bulky, cumbersome, and have the potential to harm people. To combat these issues, a newer technology has emerged – collaborative robots. A niche type of industrial robot, cobots are built on the concept of HRC, and have advanced safety features so they can work alongside humans in the same physical environment. These robots have a protective stop enabled when anything obstructs its path of motion, thereby ensuring no humans come in harm’s way. In fact, almost any task can be automated with the help of cobots, proving themselves to be of massive advantage to both large-scale and small-scale companies.
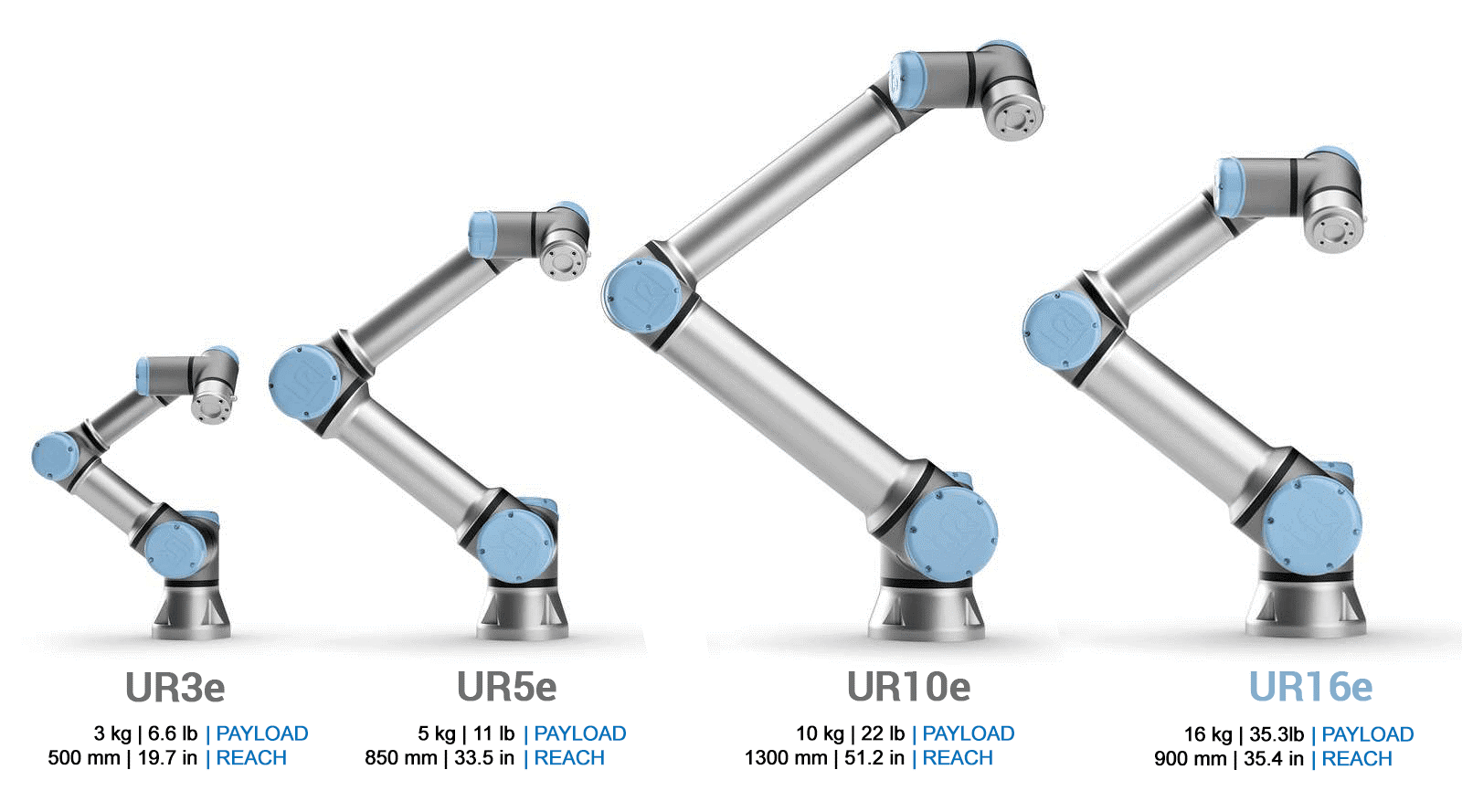 Image: A family of collaborative robots manufactured by Universal Robots
Image: A family of collaborative robots manufactured by Universal Robots
Thanks to their collaborative nature, employees can work alongside cobots ensuring that no jobs are lost. As there is no need for any protective fencing (subject to risk assessment), manufacturers do not need to sacrifice their shop floor in order to deploy this technology. Cobots can be reassigned the dull, dirty and dangerous jobs, while employees can instead work on harnessing more valuable skills. These lightweight robotic arms have low power consumption, are easy to program and set up, and are highly flexible in nature, making them the perfect automation solution for India’s manufacturing industry, and helping ensure that Indian products reach global standards of quality.
Although traditional robots have been in the market for a while, these are not ideal for SMEs and MSMEs. As traditional robots are not equipped to deal with human contact, they require suitable protective fencing around them, thus utilizing too much space which these factories cannot sacrifice. Traditional robots also require a lot of time and expertise to set up and program, proving difficult for employees to operate. Collaborative robots are thus a more convenient alternative especially for small scale manufacturers, as cobots do not require any extra fencing, are easy to operate and have a low power consumption. Human Robot Collaboration thus has a large scope for implementation and expansion in a country like India where SMEs and MSMEs play a pivotal role in its economy.
While it’s true that many traditional manufacturers initially hesitate to invest in new technologies, awareness about its benefits is slowly increasing and industries are understanding the value of cobots as an investment. Many manufacturers have already implemented unconventional automation solutions like collaborative robots, enabling them to not only grow production levels and customer satisfaction, but even upskilling and nurturing their employees. Cobots can be of great convenience to these industries, as not only do manufacturers no longer have to sacrifice the already limited shop floor, but they can also increase production levels by operating these machines throughout the day. Human Robot Collaboration has truly played a notable role in supporting the growth SMEs and MSMEs in India, and it is thus important for more manufacturers to invest in these technologies.
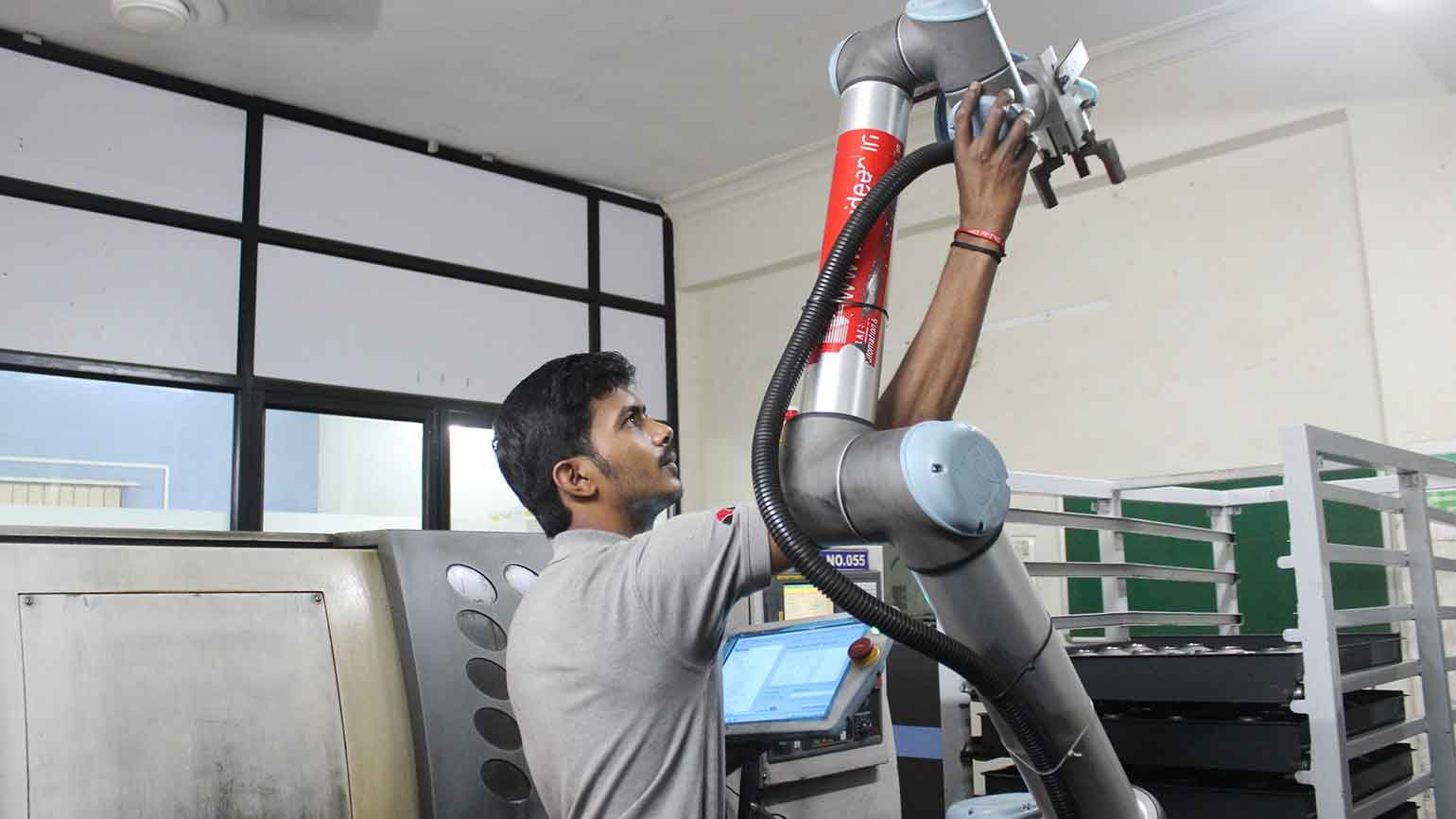 Cobots are enabling SMEs like CATI, Pune, to easily automate tasks such as CNC machine tending, even with limited shop floor space
Cobots are enabling SMEs like CATI, Pune, to easily automate tasks such as CNC machine tending, even with limited shop floor space
Many of the manufacturing industry’s leaders have already switched to collaborative and completely automated factories. Although many Indian manufacturers are slowly shifting to more collaborative methods of production, India can still be seen lagging behind other nations in this aspect. In a study from 2019, the International Federation of Robotics found that the average number of robots per 10,000 employees is about 99, with Asia being the world’s largest industrial robot market. However, India falls at about 4 robots, 25 times behind the global average. This is because traditional automation techniques are expensive, cumbersome and difficult to deploy, resulting in manufacturers becoming hesitant to deploy these. With their flexibility and easy operating, collaborative robots can be the perfect answer to this. As awareness about the benefits of cobots grows amongst Indian manufacturers, more factories will deploy collaborative methods, bringing India at par with the world’s leading automated nations.
Industry 5.0 – Collaborative Industries
The current Industry 4.0 is slowly leading up to the most exciting and technologically advanced era – Industry 5.0, or the age of collaborative industries. The emergence of Human Robot Collaboration in the fourth revolution has paved the way for factories to be completely automated, with humans only overseeing operational functions, and the addition of cobots is already enabling the industry to shift in that direction. Maintaining the human touch with cobots is necessary as automation solutions can only move forward if these machines are personalized to perform any task that a human would otherwise perform. Exploring the previously untapped resources from human ingenuity can lead to more creative solutions in the field of automation, and cobots can eventually become completely customizable.
Industry 5.0 can thus change the course of automation completely, with human and machine working together without any risk. Many of the industry’s leading manufacturing nations have already begun utilizing Industry 5.0 solutions, and Indian industries must also start engaging in new technologies to produce goods that reach the global standards of quality without sacrificing production efficiency and workplace safety. The COVID-19 pandemic has brought to light that Indian manufacturers must switch to more technologically-driven production methods that can provide a shield to these industries from any future crisis. To become a global manufacturing hub, India must play its part in driving forward new technologies and utilizing them to create more efficient and value-driven markets, and with the support provided manufacturers will be able to invest in new Industry 5.0 technologies that will eventually put India at the center of the global manufacturing landscape.







 Image: A family of collaborative robots manufactured by Universal Robots
Image: A family of collaborative robots manufactured by Universal Robots


Comments